整理iptables学习笔记,内容基本复制粘贴自参考资料整理。
工作流程
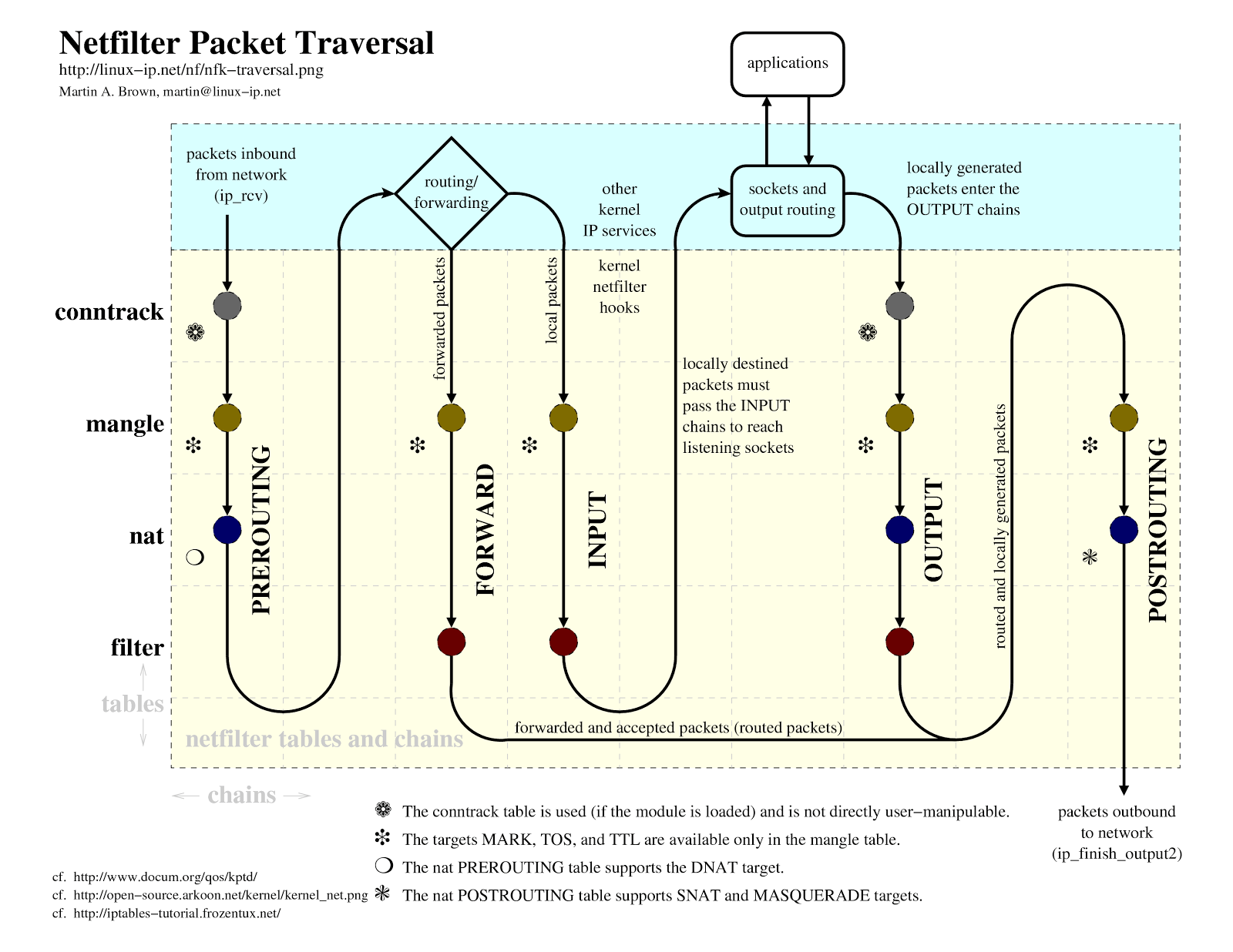
iptables能够访问底层的netfilter模块。 找到一张图,比较精简的阐述netfilter处理包的流程:
下面这张图就更加详细:
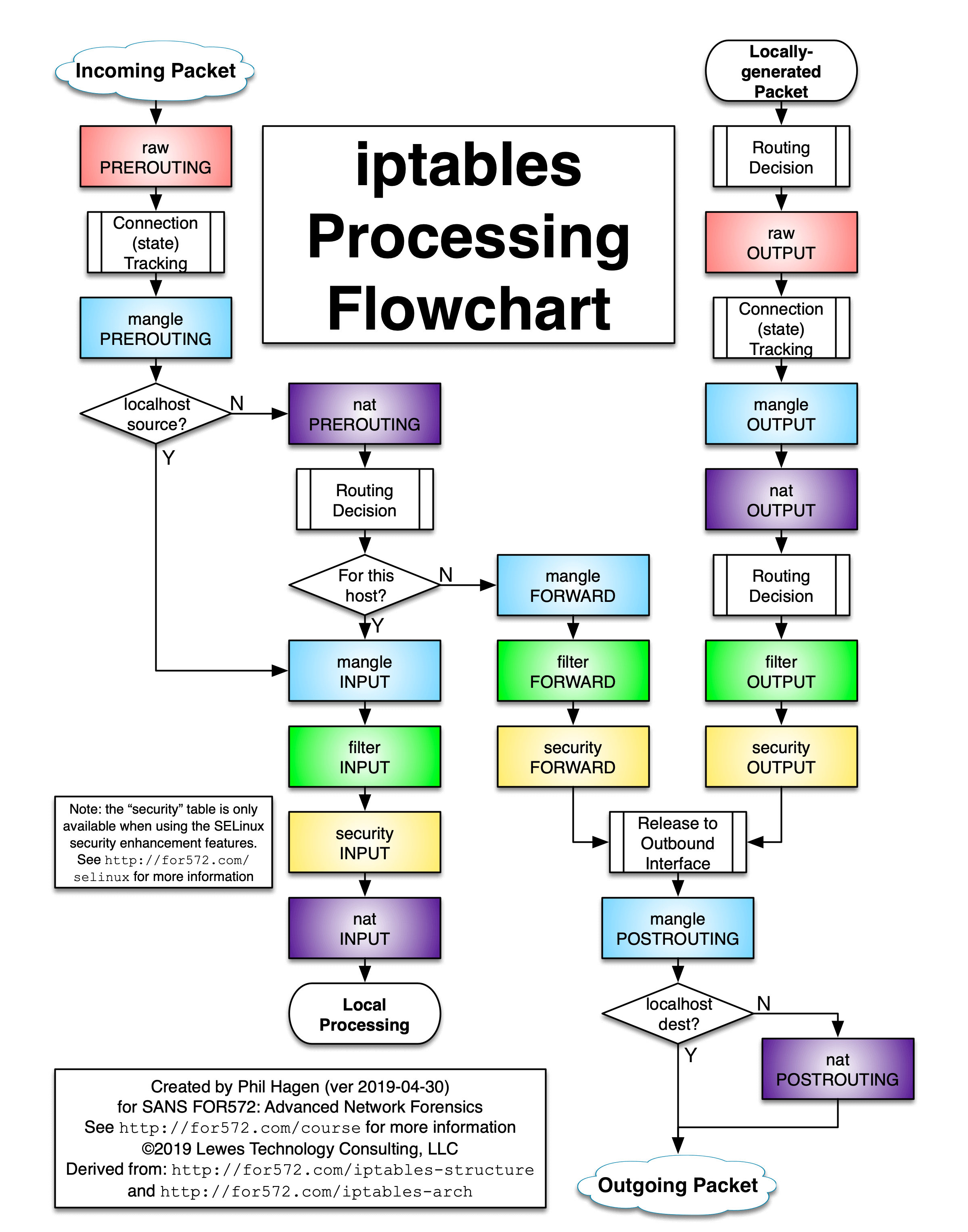
(图片来源:iptables-processing-flowchart)
表 tables
raw表:关闭nat表上启用的连接追踪机制; mangle表:拆解报文,做出修改,并重新封装 的功能; nat表:network address translation,网络地址转换功能; filter表:负责过滤功能,防火墙; security 用于强制访问控制网络规则(例如:SELinux )
优先级次序(由高而低):
raw --> mangle --> nat --> filter
大部分情况仅需要使用 filter 和 nat。
链 chains
链(chains)是数据包传播的路径,每一条链其实就是众多规则中的一个检查清单,每一条链中可以有一条或数条规则。
PREROUTING —— 进入netfilter后的数据包在进入路由判断前执行的规则 FORWARD —— 经过路由判断后,目的地不是本机的数据包执行的规则。与nat和mangle表相关联很高,与本机没有关联。 INPUT —— 要进入本机的数据包执行的规则 OUTPUT —— 由本机产生,需向外发的数据包执行的规则 POSTROUTING —— 数据包准备离开netfilter时执行的规则
本机路由转发的时候,才配置FORWARD转发链。
(/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward,0表示禁止数据包转发,1表示允许)
链的默认规则通常设置为 ACCEPT,如果想确保任何包都不能通过规则集,那么可以重置为 DROP。
表和链的关系
filter
FORWARD、INPUT、 OUTPUT
nat
PREROUTING、POSTROUTING、OUTPUT
mangle
PREROUTING、POSTROUTING、OUTPUT、INPUT、FORWARD
raw
PREROUTING、OUTPUT
规则 rules & 目标 target
数据包的过滤基于规则。规则由一个目标(数据包包匹配所有条件后的动作)和很多匹配(导致该规则可以应用的数据包所满足的条件)指定。
目标使用 -j 或者 --jump 选项指定。目标可以是用户定义的链(例如,如果条件匹配,跳转到之后的用户定义的链,继续处理)、一个内置的特定目标或者是一个目标扩展。
内置目标是 ACCEPT, DROP, QUEUE 和 RETURN,目标扩展有 REJECT 、 LOG 等。
如果目标是内置目标,数据包的命运会立刻被决定并且在当前表的数据包的处理过程会停止。
如果目标是用户定义的链,并且数据包成功穿过第二条链,目标将移动到原始链中的下一个规则。
目标扩展可以被终止(像内置目标一样)或者不终止(像用户定义链一样)。
常见的target:
ACCEPT:
允许数据包通过。
DROP:
直接丢弃数据包,不给任何回应信息,这时候客户端会感觉自己的请求泥牛入海了,过了超时时间才会有反应。
REJECT:
拒绝数据包通过,必要时会给数据发送端一个响应的信息,客户端刚请求就会收到拒绝的信息。
LOG:
在/var/log/messages文件中记录日志信息,然后将数据包传递给下一条规则。
REDIRECT:
在本机做端口映射。只适用于nat表的PREROUTING和OUTPUT链,和只调用它们的用户自定义链。
DNAT:
This target is only valid in the nat table, in the PREROUTING and OUTPUT chains, and user-defined chains which are only called from those chains.
SNAT:
This target is only valid in the nat table, in the POSTROUTING and INPUT chains, and user-defined chains which are only called from those chains.
MASQUERADE:
This target is only valid in the nat table, in the POSTROUTING chain.
RETURN:
在自定义链执行完毕后使用返回,来返回原规则链
MARK:
增加防火墙标记
3种基本路由情况

- 入站数据流向
从外界到达防火墙的数据包,先被PREROUTING规则链处理(是否修改数据包地址等),之后会进行路由选择(判断该数据包应该发往何处),如果数据包的目标主机是防火墙本机(比如说Internet用户访问防火墙主机中的web服务器的数据包),那么内核将其传给INPUT链进行处理(决定是否允许通过等),通过以后再交给系统上层的应用程序(比如Apache服务器)进行响应。
- 转发数据流向
来自外界的数据包到达防火墙后,首先被PREROUTING规则链处理,之后会进行路由选择,如果数据包的目标地址是其它外部地址(比如局域网用户通过网 关访问QQ站点的数据包),则内核将其传递给FORWARD链进行处理(是否转发或拦截),然后再交给POSTROUTING规则链(是否修改数据包的地 址等)进行处理。
- 出站数据流向
防火墙本机向外部地址发送的数据包(比如在防火墙主机中测试公网DNS服务器时),首先被OUTPUT规则链处理,之后进行路由选择,然后传递给POSTROUTING规则链(是否修改数据包的地址等)进行处理。
iptables命令和例子
常见参数
-P 设置默认策略:iptables -P INPUT (DROP|ACCEPT)
-F 清空规则链
-L 查看规则链
-A 在规则链的末尾加入新规则
-I num 在规则链的头部加入新规则
-D num 删除某一条规则
-s 匹配来源地址IP/MASK,加叹号"!"表示除这个IP外。
-d 匹配目标地址
-i 网卡名称 匹配从这块网卡流入的数据
-o 网卡名称 匹配从这块网卡流出的数据
-p 匹配协议,如tcp,udp,icmp
--dport num 匹配目标端口号
--sport num 匹配来源端口号
Options:
--ipv4 -4 Nothing (line is ignored by ip6tables-restore)
--ipv6 -6 Error (line is ignored by iptables-restore)
[!] --protocol -p proto protocol: by number or name, eg. `tcp'
[!] --source -s address[/mask][...]
source specification
[!] --destination -d address[/mask][...]
destination specification
[!] --in-interface -i input name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--jump -j target
target for rule (may load target extension)
--goto -g chain
jump to chain with no return
-match -m match
extended match (may load extension)
--numeric -n Numeric output. IP addresses and port numbers will be printed in numeric format. By default, the program will try to display them as host names, network names, or services (whenever applicable).
[!] --out-interface -o output name[+]
network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
--table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter')
--verbose -v verbose mode
--wait -w [seconds] maximum wait to acquire xtables lock before give up
--wait-interval -W [usecs] wait time to try to acquire xtables lock
default is 1 second
--line-numbers print line numbers when listing
--exact -x expand numbers (display exact values)
输出一个链的详情:
iptables -nvL <chain>
iptables match / target有一堆扩展,参见:iptables-extensions。 可以简单查看match / target的参数:
[root@host143 ~]# iptables -m iprange --help
iprange match options:
[!] --src-range ip[-ip] Match source IP in the specified range
[!] --dst-range ip[-ip] Match destination IP in the specified range
[root@host143 ~]# iptables -j DNAT --help
DNAT target options:
--to-destination [<ipaddr>[-<ipaddr>]][:port[-port]]
Address to map destination to.
[--random] [--persistent]
使用iptables,要确定操作的chain、过滤条件(ip、端口、协议)、目标动作。
前置操作
清除所有规则
tables -F
设置链的默认策略(默认是ACCEPT)
iptables -P FORWARD DROP
保存规则
iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
或者
service iptables save
导入iptables-save保存的规则
iptables-restore < files_saved_by_iptables-save
禁止转发
禁止转发源IP地址为192.168.1.20-192.168.1.99的TCP数据包
# 因为是“转发”,使用FORWARD链
# -A 在某个chain后面增加规则
# -p 协议
# -j 跳转目标
# -m match匹配,iprange是扩展,支持--dst-range和--src-range
iptables -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 192.168.0.20-192.168.0.99 -p tcp -j DROP
这里使用了iptables match扩展的iprange。
MAC和地址绑定
iptables –A FORWARD -s 192.168.30.20 –m mac --mac-source 00:11:5B:EF:7A:D8 -j DROP
阻止某个ip入站
iptables -A INPUT -s x.x.x.x -j DROP
允许所有外部http的连接请求
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# 只对已经建立连接的出站
# 如果是ftp,则还要增加 RELATED
iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 80 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
这里使用了match的state模块。为了解决一个安全问题:怎样判断这些报文是为了回应我们之前发出的报文,还是主动向我们发送的报文呢? (因为发送过来的报文并不总是为了响应我们,也有可能是为了主动攻击我们。)
state是conntrack模块的子集,支持INVALID, ESTABLISHED, NEW, RELATED or UNTRACKED。
The “state” extension is a subset of the “conntrack” module. “state” allows access to the connection tracking state for this packet. [!] –state state Where state is a comma separated list of the connection states to match. Only a subset of the states unterstood by “conntrack” are recognized: INVALID, ESTABLISHED, NEW, RELATED or UNTRACKED. For their description, see the “conntrack” heading in this manpage.
state状态如下:
- NEW:连接中的第一个包
- ESTABLISHED:把NEW状态包后面的包的状态理解为ESTABLISHED,表示连接已建立
- RELATED:正在建立一个新的连接,这个连接是和一个已建立的连接相关的。比如,FTP data transfer,ICMP error 和一个TCP或UDP连接相关
- INVALID:如果一个包没有办法被识别,或者这个包没有任何状态
- UNTRACKED:当报文的状态为Untracked时通常表示无法找到相关的连接。
multiport合并多个端口的规则
match扩展支持multiport,使用--dports和--sports。这样多个端口能够合并为一条规则。
# 允许外部的多个端口访问本机
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80,443 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --sports 22,80,443 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
允许从本地发起的HTTPS连接请求
因为出站规则,先设置OUPUT链,对应的连接状态是NEW、ESTABLISHED。 然后设置INPUT链,对应的连接状态是ESTABLISHED。
iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --sport 443 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
DNAT
扩展target。
防火墙收到来自外网的数据包后,会将该数据包的目的IP地址进行替换(源IP地址不变),重新转发到内网的主机。
修改目的ip地址的原因一般就是为了改变包发送的目的地,让包走出去,而不是留下来,所以在iptables中,DNAT是在入口,也即PREROUTING链中发挥作用,以便让包进入FORWARD表。
# 把所有指向11.22.33.44的http流量转到192.168.99.99
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 11.22.33.44 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.99.99:8080
参数如下:
–to-destination [ipaddr[-ipaddr]][:port[-port]]
which can specify a single new destination IP address, an inclusive range of IP addresses. Optionally a port range, if the rule also specifies one of the following protocols: tcp, udp, dccp or sctp. If no port range is specified, then the destination port will never be modified. If no IP address is specified then only the destination port will be modified. In Kernels up to 2.6.10 you can add several –to-destination options. For those kernels, if you specify more than one destination address, either via an address range or multiple –to-destination options, a simple round-robin (one after another in cycle) load balancing takes place between these addresses. Later Kernels (>= 2.6.11-rc1) don’t have the ability to NAT to multiple ranges anymore.
–random
If option –random is used then port mapping will be randomized (kernel >= 2.6.22).
–persistent
Gives a client the same source-/destination-address for each connection. This supersedes the SAME target. Support for persistent mappings is available from 2.6.29-rc2.
作用:
- 没有公网IP而对外提供服务场景,相当于端口映射
- 保护真实主机ip的作用
SNAT
扩展target。可以代理上网的功能。
当内网数据包到达防火墙后,防火墙会使用外部地址替换掉数据包的源IP地址(目的IP地址不变),使网络内部主机能够与网络外部主机通信。
修改源ip地址的目的一般都是为了让这个包能再回到自己这里,所以在iptables中,SNAT是在出口,也即POSTROUTING链发挥作用。
假设防火墙两张网卡,一张eth0对接外网,ip为1.1.1.1。
另一张eth1,对接内网。内网网段192.168.100.0/24都使用这个网关访问互联网:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 1.1.1.1
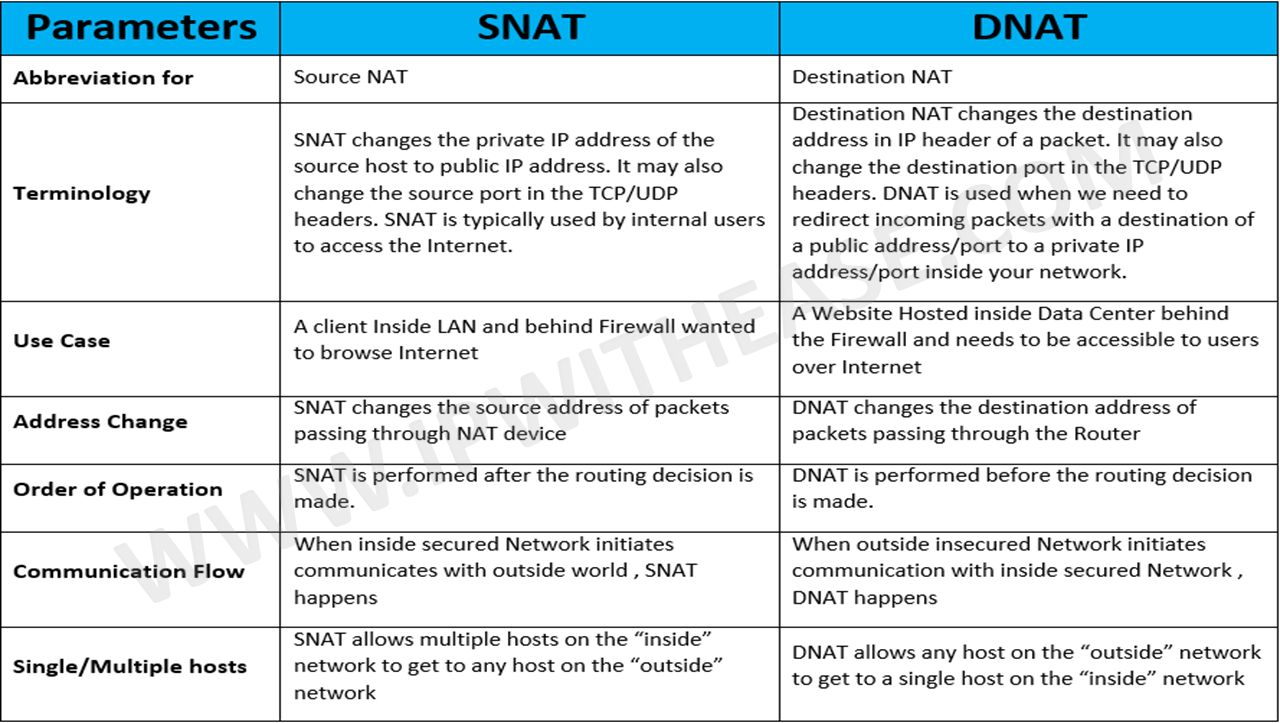
贴一张网上对比snat和dnat的表格:
MASQUERADE
扩展target。 适用于外网ip地址非固定的情况。用发送数据的网卡上的IP来替换源IP,因此,对于那些IP不固定的场合,比如拨号网络或者通过dhcp分配IP的情况。
例如上面SNAT的例子,如果eth0使用adsl方式上网:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -j MASQUERADE
端口转发
假设对外使用30022作为ssh端口(默认为22)
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -d 192.168.100.1 --dport 30022 -j DNAT --to 192.168.100.1:22
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 30022 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 30022 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ping相关
允许内网ping外网
iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-reply -j ACCEPT
允许外网ping内网
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-reply -j ACCEPT
负载均衡
把80端口的流量负载均衡到3台机器上:
# -m nth:使用统计模块,并且是轮询模式,需要指定两个参数:
# --every n:每n个packet轮询一次
# --packet p:设置初始化计数
# 从第 p 个包开始,每 n 个包执行该规则
iptables -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m nth --counter 0 --every 3 --packet 0 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.100.101:8080
iptables -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m nth --counter 0 --every 3 --packet 1 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.100.102:8080
iptables -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m nth --counter 0 --every 3 --packet 2 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.100.103:8080
这里使用了statistic模块。支持两种负载均衡模式:随机和轮询。
–mode mode Set the matching mode of the matching rule, supported modes are random and nth. [!] –probability p Set the probability for a packet to be randomly matched. It only works with the random mode. p must be within 0.0 and 1.0. The supported granularity is in 1/2147483648th increments. [!] –every n Match one packet every nth packet. It works only with the nth mode (see also the –packet option). –packet p Set the initial counter value (0 <= p <= n-1, default 0) for the nth mode.
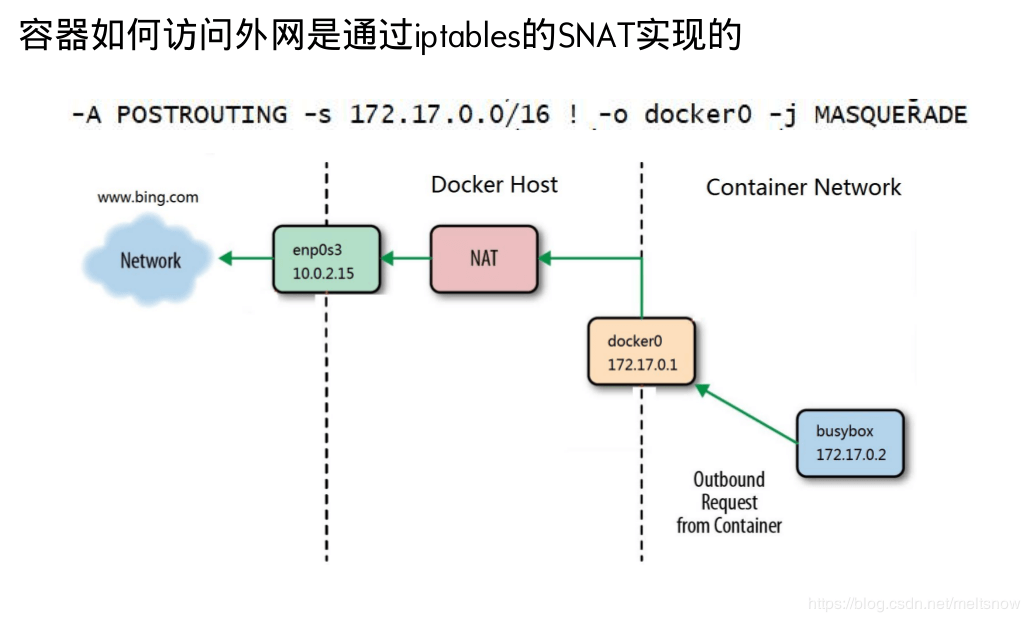
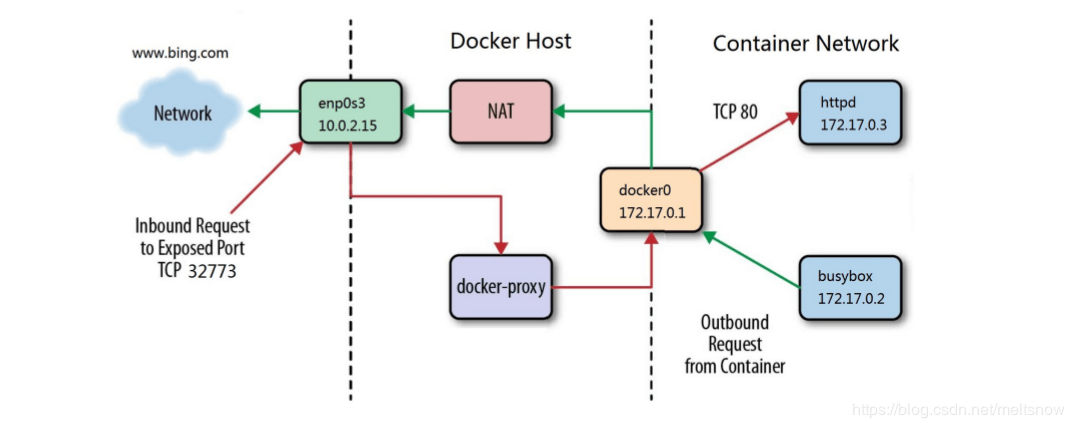
docker iptables使用snat访问外网
网上看到的图,形象生动: