AbstractSecurityInterceptor是安全拦截器的基类。 FilterSecurityInterceptor是鉴权相关的filter。 InterceptorStatusToken是两者通信的渠道。
AbstractSecurityInterceptor
在理解FilterSecurityInterceptor之前,需要先深入AbstractSecurityInterceptor。
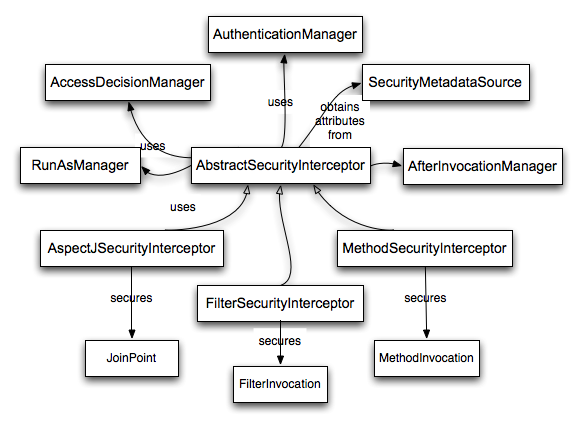
AbstractSecurityInterceptor是安全拦截器的基类。 涉及成员:
- AuthenticationManager:认证
- AccessDecisionManager:鉴权
- SecurityMetadataSource:获取属性列表
- RunAsManager:替换认证用户
- AfterInvocationManager:鉴权完成后续处理
核心方法:
- beforeInvocation
- finallyInvocation
- afterInvocation
工作流程:
- 从SecurityContextHolder获取Authentication对象
- 通过SecurityMetadataSource判断这个secure object是安全的还是公开的
- 对于安全请求:
- 如果Authentication.isAuthenticated()为false,或者alwaysReauthenticate为true,就交给AuthenticationManager验证。返回结果更新到SecurityContextHolder。
- AccessDecisionManager判断该请求的授权
- RunAsManager尝试切换用户执行
- 交给子类执行。子类执行完毕后,返回InterceptorStatusToken对象。AbstractSecurityInterceptor#finallyInvocation()用于清理现场。
- 子类调用AbstractSecurityInterceptor#afterInvocation()
- If the RunAsManager replaced the Authentication object, return the SecurityContextHolder to the object that existed after the call to AuthenticationManager.
- AfterInvocationManager处理
- 对于公开请求:
- 子类返回InterceptorStatusToken对象。
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}
protected Object afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token, Object returnedObject) {
if (token == null) {
// public object
return returnedObject;
}
finallyInvocation(token); // continue to clean in this method for passivity
if (afterInvocationManager != null) {
// Attempt after invocation handling
try {
returnedObject = afterInvocationManager.decide(token.getSecurityContext()
.getAuthentication(), token.getSecureObject(), token
.getAttributes(), returnedObject);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
AuthorizationFailureEvent event = new AuthorizationFailureEvent(
token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), token
.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(),
accessDeniedException);
publishEvent(event);
throw accessDeniedException;
}
}
return returnedObject;
}
finallyInvocation清理AbstractSecurityInterceptor产生的上下文。
要在secure object调用之后、afterInvocation调用之前使用finallyInvocation。
protected void finallyInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token) {
// token == null 为public invocation
if (token != null && token.isContextHolderRefreshRequired()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Reverting to original Authentication: "
+ token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication());
}
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(token.getSecurityContext());
}
}
InterceptorStatusToken是security拦截器的状态抽象。 AbstractSecurityInterceptor和它的子类通过InterceptorStatusToken来通信。
public class InterceptorStatusToken {
private SecurityContext securityContext;
private Collection<ConfigAttribute> attr;
private Object secureObject;
private boolean contextHolderRefreshRequired;
FilterSecurityInterceptor
处理鉴权的子类,负责触发secure object调用。
public class FilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {}
有了AbstractSecurityInterceptor的基础,理解起来简单多。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// AbstractSecurityInterceptor前置操作
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
// secure object invocation
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
// AbstractSecurityInterceptor清理操作
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
// AbstractSecurityInterceptor后置操作
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
AccessDecisionVoter和AccessDecisionManager
AccessDecisionVoter是投票者,需要对Authentication请求投票,有3种结果:
int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1;
int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0;
int ACCESS_DENIED = -1;
AccessDecisionVoter有多种内置实现。
RoleVoter很简单,直接根据传入属性的前缀判断是否允许访问:
public class RoleVoter implements AccessDecisionVoter<Object> {
private String rolePrefix = "ROLE_";
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) {
if ((attribute.getAttribute() != null)
&& attribute.getAttribute().startsWith(getRolePrefix())) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public int vote(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
if (authentication == null) {
return ACCESS_DENIED;
}
int result = ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = extractAuthorities(authentication);
for (ConfigAttribute attribute : attributes) {
if (this.supports(attribute)) {
result = ACCESS_DENIED;
// Attempt to find a matching granted authority
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
if (attribute.getAttribute().equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
return ACCESS_GRANTED;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
AccessDecisionManager是判断有无权限的管理器。有3种实现:
- AffirmativeBased:任意一个voter返回同意则允许访问。
- ConsensusBased:多数服从少数。如果同意和拒绝票数一样,则根据
allowIfEqualGrantedDeniedDecisions判断。 - UnanimousBased:一票否决。如果voter都弃权,则根据
allowIfAllAbstainDecisions判断。
RunAsManager
RunAsManager是个有意思的设计,可以临时替换SecurityContext中的Authentication对象。 有了RunAsManager,可以支持2层安全模式。 一层是public,面向外部调用者。 另一层是private,并且只提供给public层使用。private层的方法也收到安全约束,因此需要配置特别的授权GrantedAuthority(这些授权不会暴露到外部调用者)。